“Cyber Warfare: From Espionage to War A Journey Through Time”
With the massive technological advancements, the boundaries of warfare have expanded to encompass cyberspace, where “cyber warfare” has emerged as an increasingly serious threat to individuals, institutions, and countries.
The line between cyber and traditional wars has blurred for a while but recent activities in the region made it clear that cyberwars is becoming a dangerous and can lead to harming humans.
In this blog, we will dive into a journey through the world of cyber warfare, seeking to understand its nature, history, impacts, types, evolution, and some solutions to confront its risks.
But first, let us acquaint ourselves with the concept of warfare in general and how it evolves through the years.
Wars and War Generations
In general, war is a state of conflict between two or more parties using weapons due to differences between them, whether differences in interests or differing perspectives that might involve political disputes.
Generations of War
Wars are traditionally classified into generations, each with their own characteristics and features.
First-generation wars are characterized using traditional tactics such as armies and simple weapons.
Second Generation Wars included the use of advanced technology and the expansion of global conflicts e.g., World War I.
Third Generation Wars: Focused on rapid and sudden use, integrating different armed forces to overcome the enemy.
Fourth Generation Wars: Known as proxy wars, they are characterized using technology in international conflicts, where the lines between war and politics are blurred.
Fifth Generation Wars: Focus on indirect attacks and the use of soft power alongside military force. This type of warfare focuses on influencing public opinion and achieving political and economic objectives rather than relying primarily on military force.
And now we move on to cyber warfare.
Cyber Warfare: An Overview
Cyberwarfare is defined as conflicts in which digital tools and technologies are used to disable, misinform, sabotage, or cause harm to adversaries, steal data, or even launch wide-scale electronic attacks.
The concept of cyber warfare involves military-led electronic attacks aimed at penetrating global electronic systems and anything reliant on technology, causing damage to computer devices and devices connected to the internet, which could lead to catastrophic consequences like nuclear wars if successful.
Relationship of Cyber Warfare to War Generations:
Cyber warfare represents an extension of modern warfare, where technology and the internet are used to execute attacks and impact the digital infrastructure of adversaries.
Impact of Cyber Warfare Compared to Physical Warfare:
Cyber warfare is characterized by its precise effects, yet it can be equally destructive, targeting vital infrastructure such as energy networks, financial systems, and communication networks.
The effects of cyber warfare differ from those of traditional physical warfare in several aspects:
No Geographic Boundaries: Cyber-attacks are launched in cyberspace and are not limited to specific geographic borders, making it difficult to pinpoint the location and source of the attack.
Precision Impact: Cyber battle focuses on targeting specific systems or sensitive data, causing precise but potentially devastating damage.
Indirect Impact: Cyber-attacks can disrupt vital infrastructure like energy networks, communications, and financial systems, leading to widespread chaos, economic downturns, and social disruptions.
Difficulty in Attribution: It is often challenging to identify the responsible party behind cyber-attacks, leading to increased tensions between states and undermining trust in international relations.
Proliferation of Weapons and Tactics: Unethical attackers find it easy to obtain cyber weapons and tactics, increasing the likelihood of global cyber conflicts.
Overall, while cyber battle may not result in physical destruction on the same scale as traditional warfare, its effects can be far-reaching and profound, impacting critical infrastructure, economies, and international relations.

Types of Cyber Warfare:
Cyber-espionage: involves gathering secret and sensitive information from government agencies, companies, or individuals for intelligence purposes.
Cyber Sabotage: Seeks to target critical infrastructure with the aim of disrupting operations or causing damage.
Cyber Propaganda: uses social media, fake news, and online disinformation campaigns to manipulate public opinion, spread discord, and destabilize governments.
Cyberterrorism involves cyberattacks to spread fear, cause harm, promote, or propagate political or religious ideas.
Evolution of Cyber Armies Over Time:
The inception of cyber armies dates back to the dawn of the computer networking and military computing eras. Initially, efforts focused on defensive measures to protect military systems from penetration and sabotage.
With technological advancements, countries have recognized the potential of cyber-attacks in offensive operations and intelligence-gathering efforts.

A Brief History of Cyber Armies and Their Types:
Early Developments (1960s–1980s): During this period, the focus was on defensive measures to protect military systems, primarily through the development of secure communication channels and encryption techniques to safeguard sensitive information.
Emergence of Offensive Capabilities (1990s–Early 21st Century): Countries began exploring offensive cyber capabilities, with major powers investing in cyber battle programs to gain a strategic advantage in conflicts. Cyber espionage and surveillance became prevalent, with intelligence agencies targeting foreign governments, military institutions, and defense contractors to gather intelligence.
Modern Cyber Warfare (2010–Present): Increased Intensity of Cyber Attacks where the first decade of the 21st century witnessed a surge in cyber battle activities, with state-sponsored actors launching prominent cyber-attacks.
This evolution highlights the transition from a focus on defensive measures to offensive capabilities, marking a significant shift in the landscape of cyber battle for the following reasons:
Integration of Cyber Capabilities: Countries have recognized the importance of cyberspace as a new battleground and have integrated cyber capabilities into their military strategies.
Evolution of the Cyber Army Arsenal: Cyber armies have expanded their arsenals to include sophisticated malware programs, zero-day exploit programs, and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) capable of disrupting vital infrastructure and conducting espionage operations.
Hybrid Warfare: Tactics of hybrid warfare, which combine traditional military operations with cyber-attacks and disinformation campaigns, have become prevalent in conflicts such as the Ukrainian War.
In conclusion,
cyber warfare poses a significant and evolving threat in the modern World, necessitating the enhancement of cybersecurity defenses, strengthening international cooperation and standards, and investing in cybersecurity awareness, research, and development to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Share this article:
Popular

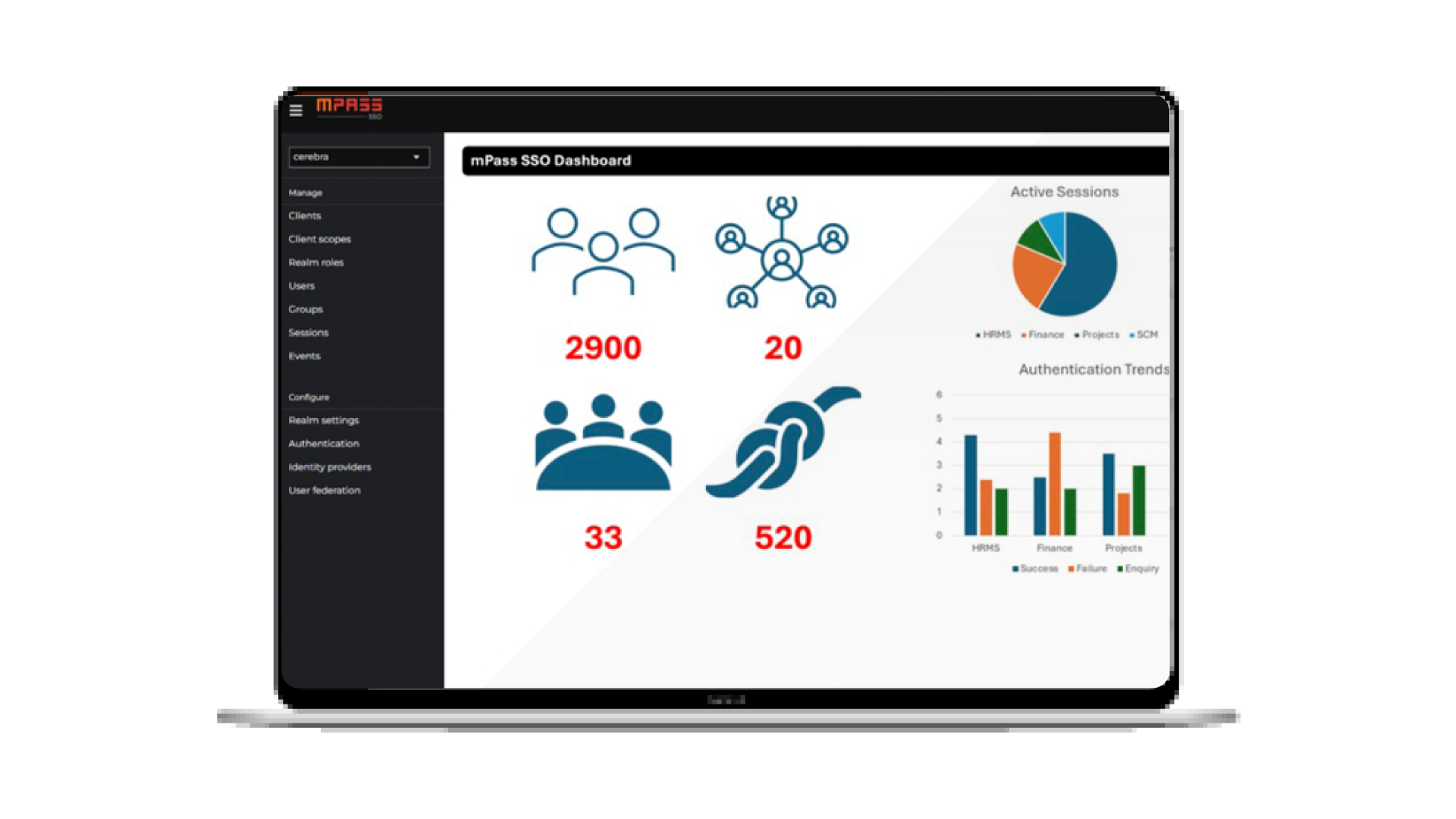
Revolutionize Enterprise Communication Platform with LinQ2
Revolutionize Enterprise Communication Platform with LinQ2 In today’s fast-paced business environment, enterprise communication platform is the backbone of success. Whether reaching customers, coordinating with employees, or automating notifications, having an effective enterprise communication platform is essential. Cerebra’s LinQ2 stands out as the ultimate solution, offering a multi-channel notification platform tailored for businesses of all sizes. Why Enterprise Communication Platform Is Essential for Business Growth? Efficient enterprise communication platform ensures businesses can stay connected with their customers and teams in real time. Poor communication systems often lead to missed opportunities, customer dissatisfaction, and delays in internal operations. Key Features of LinQ2 ...
11th Mar 2025
Deepfake in Phishing: Challenges and Solutions
In the era of advanced technologies, especially with the explosive adoption of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI), deepfake has emerged as one of the most significant challenges in cybersecurity. This technology relies on Artificial Intelligence, specifically deep learning and the use of GenAI, to create fake yet highly realistic content that is difficult to detect. Deepfake serves as a versatile tool spanning applications from entertainment to cybersecurity. However, its misuse can pose severe risks, especially in phishing schemes. What is Deepfake? Synthetic media refers to a technology that leverages deep learning algorithms to create ...
19th Dec 2024
AI Governance: Opportunities and Challenges in Cybersecurity
AI Governance: Opportunities and Challenges in Cybersecurity With the increasing reliance on AI technologies in various fields, AI Governance has become a key factor to ensure system integrity and data protection. This governance plays an essential role in enhancing confidence in modern technology and ensuring that it is used responsibly. It has been almost two years since OpenAI’s ChatGPT went viral, igniting widespread interest in artificial intelligence (AI) and setting off a wave of technological and investment growth in the field. Academic and technical investments in artificial intelligence: The advancements in AI since then have been staggering, with exponential increases ...
14th Nov 2024
Keeping Our Kids Safe Online
A Guide For Keeping Your Kids Safe Online Parents and all who are concerned about the well-being of our young kids in this digital world. Today we will discuss a topic of utmost importance: digital safety for kids. Yes, the Internet can be a very dangerous place for our young kids , especially with the spread of phishing scams. So, let us dive deeper and present to you, in this comprehensive article, a comprehensive guide on digital safety for kids. What every parent needs to pay attention to. Internet risks for kids: The internet has become a big part of ...
17th Jul 2024
Could you be hacked through Slack?
Could you be hacked through Slack? The usage of collaboration platforms such as Microsoft Teams and Slack has significantly increased, with nearly 80% of employees utilizing them. These platforms are designed to be convenient and easily manageable for daily conversations within organizations. However, what makes them easy and convenient also renders them vulnerable to cyber threats and attacks. In 2021, for instance, 780 gigabytes of data from the gaming giant Electronic Arts (EA) were breached through Slack! During the same year, a security vulnerability in Microsoft Teams was exploited to launch a widespread cyber attack on ...
12th Jun 2024
Tips To Be Cyber Protected While Traveling
Goodbye worry! A safe journey in the digital world With all the modern wonders of the digital world, we trust communication technologies on our journeys. There is no doubt that the travel experience is always more beautiful and enjoyable, but it can also pose a range of risks, especially when it comes to cybersecurity. Travelers may fall victim to phishing, Wi-Fi network spying, and theft of their personal data, which can make their journey filled with worries and tension. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, it is essential for travelers to follow some guidelines to protect their devices and ...
1st Apr 2024
Push Authentication: A New Era in Multi-Factor Authentication
Want To Say Goodbye To Passwords and OTP Codes? Discover Push Authentication! It is easy for your password to be compromised through phishing attacks, even if it meets the cybersecurity strong password standards and is difficult to predict So we must get to know the technique of Push based Authentication. Some may recommend that you use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to increase your security. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA is the process of logging into your account through multiple steps. It requires you to enter more information, not just your password. But there is another obstacle that arises when using such ...
14th Feb 2024
The Difference Between Phishing Attacks
The Difference Between Phishing Attacks Phishing attacks are harmful attacks used by criminals to steal personal and financial information from individuals and businesses. Attacks on individuals and businesses are becoming more common as we use the internet and technology more often in our daily lives. Phishing attacks involve the use of dishonesty and fraudulent methods to fool consumers into believing they are interacting with the trustworthiness of an unsuspecting destination, such as banks, email companies, or social media platforms. But what is the difference between phishing attacks? How can individuals and organizations protect themselves from such attacks? That is what ...
17th Jul 2023
Understanding of the Vishing Meaning
Understanding of the Vishing Meaning Vishing, a combination of “voice” and “phishing,” is a sophisticated form of cybercrime that exploits voice communication to trick individuals and extract sensitive information. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the meaning of it, the dangers associated with it, and effective methods to protect yourself against these malicious attacks. What is Vishing meaning? Vishing refers to the fraudulent practice of using telephone services to trick individuals into revealing personal and financial information. Scammers often pose as trusted organizations or individuals to gain their victims’ trust. By using social engineering tactics and manipulating ...
5th Jul 2023